Fuses protect your vehicle’s electrical system from overloading. If electrical parts in your vehicle are not working, the system may have been overloaded and blown a fuse. Before you replace or repair any electrical parts, check the appropriate fuses.
The following charts tell you which fuses protect each electrical part of your vehicle. If a fuse blows, all the parts of your vehicle that use that circuit will not work.
Once you have determined which fuses to check, follow the procedures under Checking and Replacing Fuses further down this page.
1983-1992 Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel
The fuse panel is behind a panel on the front of the lower dash to the left of the steering wheel. I found a lot of conflicting information and diagrams from 1983-1992. The good thing is that your dash panel should have a decal on the back side of it that shows the fuse box diagram. If it does not, here are some examples.

1985 Ford Ranger Fuse Panel Diagram:
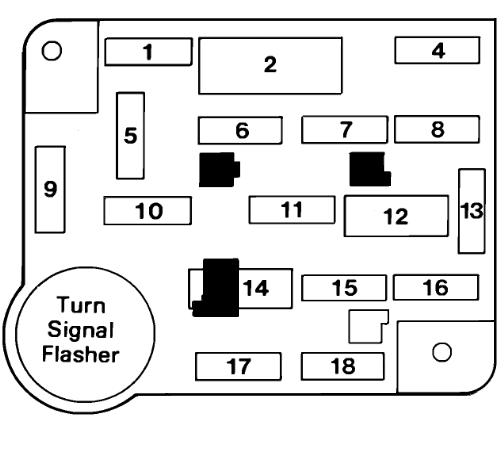
1989 Ford Ranger Fuse Panel Diagram:
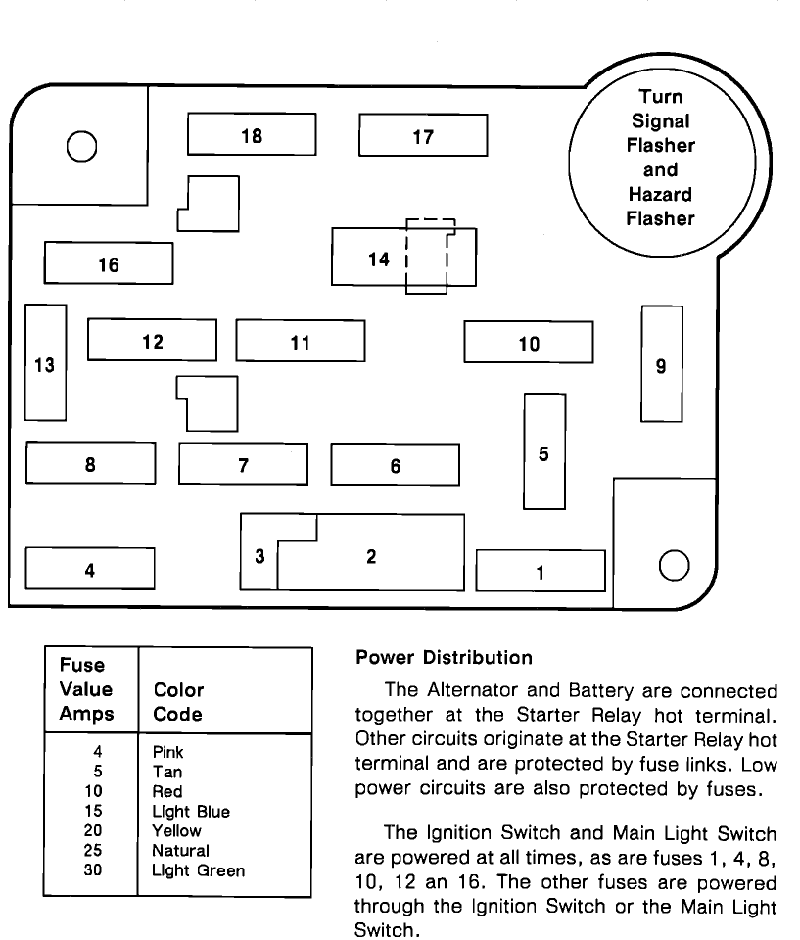
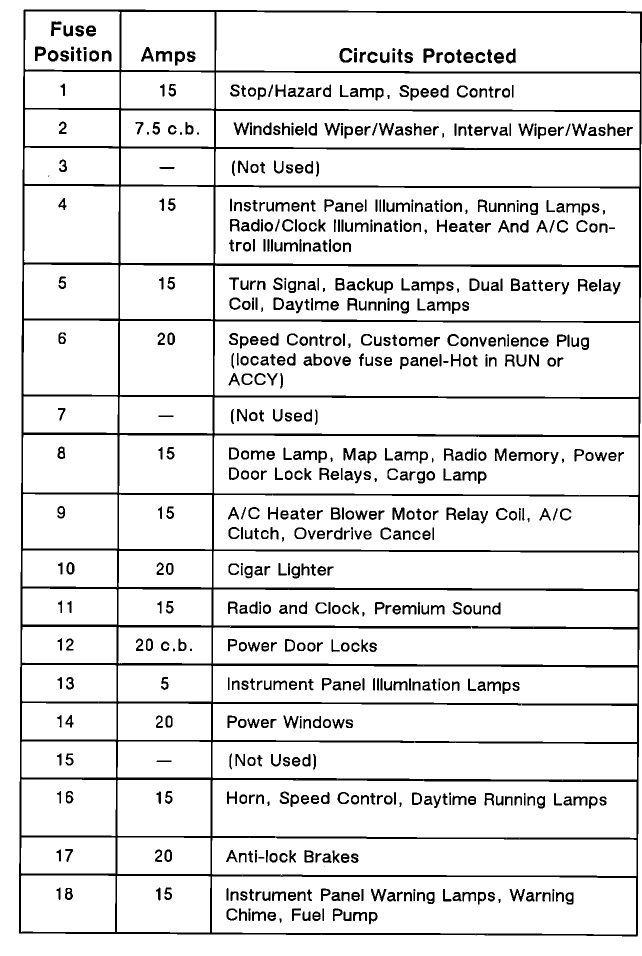
1989-1992 Ford Ranger Fuse Panel Diagram:
It would seem that the later 1989-1992 Ford Ranger fuse box could use this
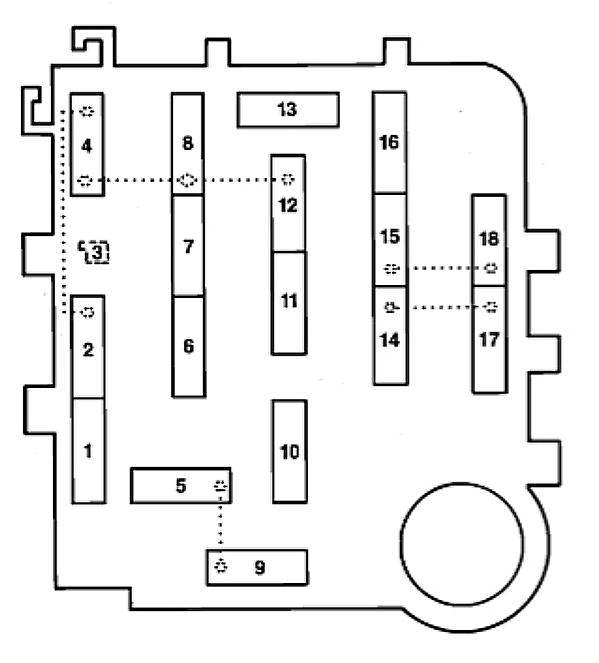
The alternator is connected to maxi-fuses within the power distribution box which is then connected together with the battery at the starter relay hot terminal. Circuits and components are protected by maxi-fuses. Lower power circuits are also protected by fuses.
The ignition switch and light switch are powered at all times, as are fuse 1, 10, 11, 17 and circuit breaker 14. The other fuses are powered through the ignition switch, or the main light switch.
Position 3 is not used and covered by circuit breaker 2.
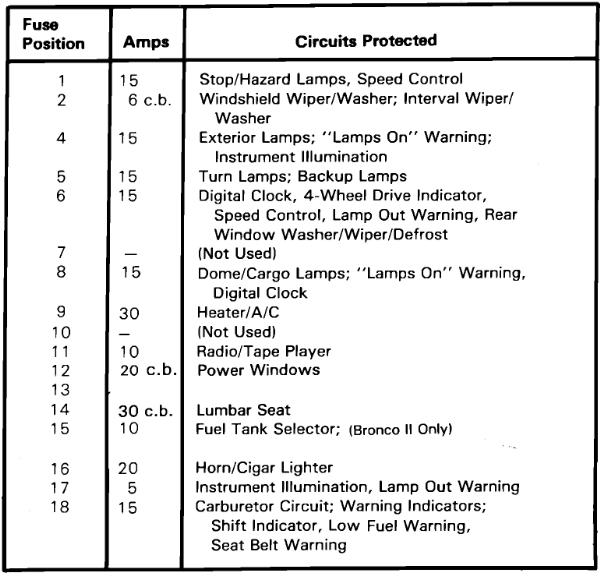
| No. |
AMPS |
Protected Circuits |
| 1 | 15 | Dome/Courtesy Light, Radio |
| 2 | 6 | Circuit Breaker: Front Washer/Wiper |
| 3 | – | Not Used |
| 4 | 15 | Four-Way Flash, Stoplights, Speed Control Inhibit |
| 5 | 15 | Turn Signals, Back-Up Lights, Turn Indicator, Rear Defrost Control, Brake Fluid Level Sensor |
| 6 | 15 | Rear Window Wiper and Washer |
| 7 | 10 | A/C Switches, Clutch Coil |
| 8 | 20 | Horns |
| 9 | 30 | Blower Motor |
| 10 | 15 | Parking Lights, License Lights, Engine Compartment Lamp, Lamps on Warning |
| 11 | 15 | Speed Control Amplifier & Radio, All Wheel Drive |
| 12 | 20 | Circuit Breaker: Cigar Lighters, Flash-to-Pass, Multi-Function Switch |
| 13 | 10 | Instrument Panel Illumination, Park/H Light Hot |
| 14 | 20 | Power Windows, Lumbar |
| 30 | 1991-1992: Power Windows, Lumbar | |
| 15 | 20 | Rear Anti-Lock Brake (RABS) Module |
| 16 | 15 | Premium Radio Amplifier |
| 17 | 20 | Cluster Warning Light, All Wheel Drive |
| 15 | Electric Shift Control, Lamps on Warning, Low Oil Level Relay, Instrument Cluster | |
| 18 | 10 | HEGO Heater |
| 15 | Shift Indicator, Low Fuel Warning, Seat Belt Warning, Carburetor Circuit: Warning Indicator |
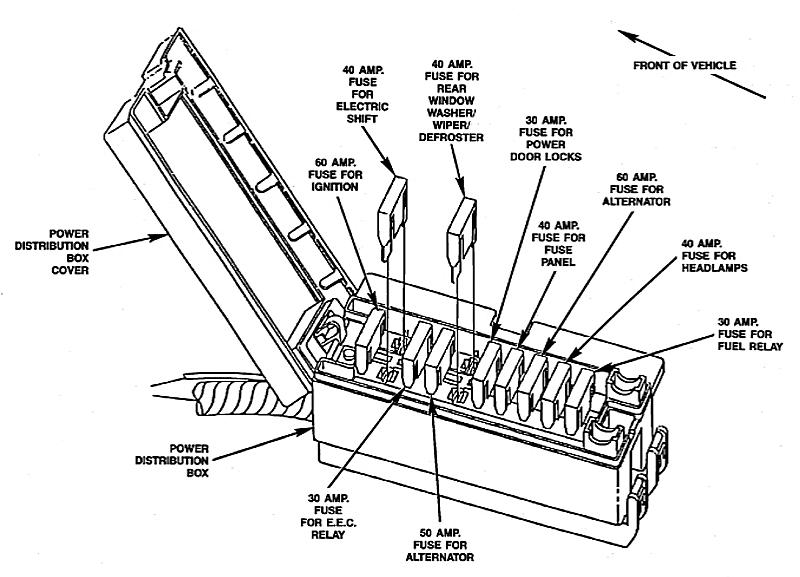
Engine Compartment Fuse Box
Your Ford Ranger may have a power distribution box (fuse box) in the engine compartment. If so, here is a diagram that should match.
| No. |
A |
Protected Circuits |
| 1 | 60 | Ignition |
| 2 | 40 | Electric Shift |
| 3 | 30 | E.E.C. Relay |
| 4 | 50 | Alternator |
| 5 | 40 | Rear Window Washer / Wiper / Defroster |
| 6 | 30 | Power Door Locks |
| 7 | 40 | Fuse Panel |
| 8 | 60 | Alternator |
| 9 | 40 | Headlamps |
| 10 | 30 | Fuel Relay |
Checking and Replacing Fuses
If you need to check a fuse, follow these steps:
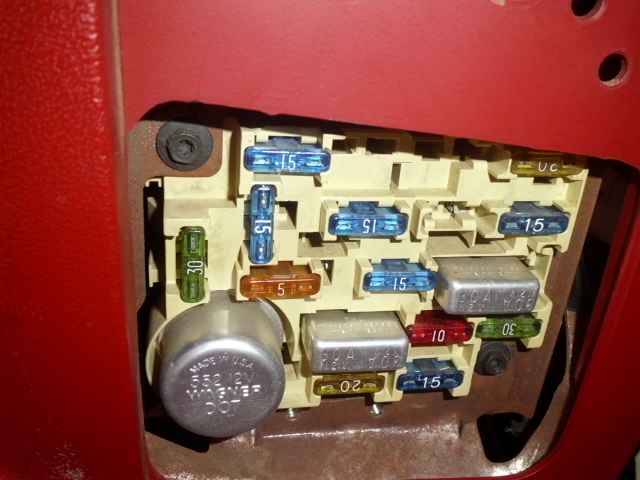
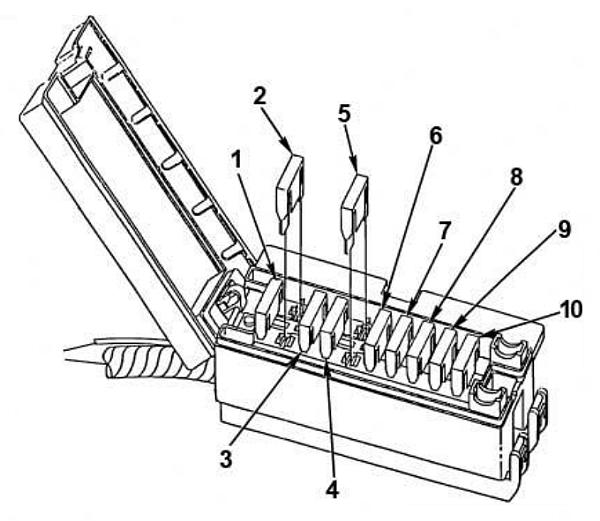
1. Find the fuse panel, which is located in the left end of the instrument panel. The power distribution box (described earlier in this section) is found in the engine compartment, mounted on a bracket attached to the drivers side fender apron.
To access the fuse panel, remove the fuse panel cover by inserting your finger in the divot and pulling on the cover. The underside of the cover contains four spare fuses. A fuse pulling tool is located in the lower right corner of the fuse panel in case you need to replace a blown fuse.
Color Coded: The spare fuses for your vehicle are color coded as follows:
- 10 amp — red
- 15 amp — light blue
- 20 amp — natural
- 30 amp — light green.
See further down on this page for examples
2. On the fuse panel cover, find the number of the fuse you want to check. The diagram on the cover tells you where to
locate the fuse on the panel.
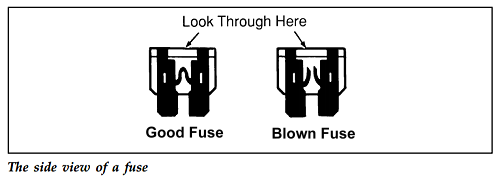
3. Check the fuse to see if it is blown. Look through the clear side of the fuse to see if the metal wire inside is separated. If it is, the fuse is blown and should be replaced.
Another method for testing fuses is to use a Bussmann fuse tester. There’s no need to remove the fuse from the holder. You simply adjust the prong width on the tester to line up with the bare metal spots on the end of the fuse, and then watch for the indicator light to glow signaling that the fuse is good.

4. Replace the fuse with one that has the right amperage rating
*WARNING Always replace a fuse with one that has the specified amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can cause severe wire damage and could start a fire.
5. Put the fuse panel cover back on.
Even after you replace a fuse, it will continue to blow if you do not find what caused the overload. If the fuse continues to blow, have your electrical system checked.
Fuse Color / Ratings:
As mentioned above, fuses are color coded to their AMP rating. See the image below for examples.