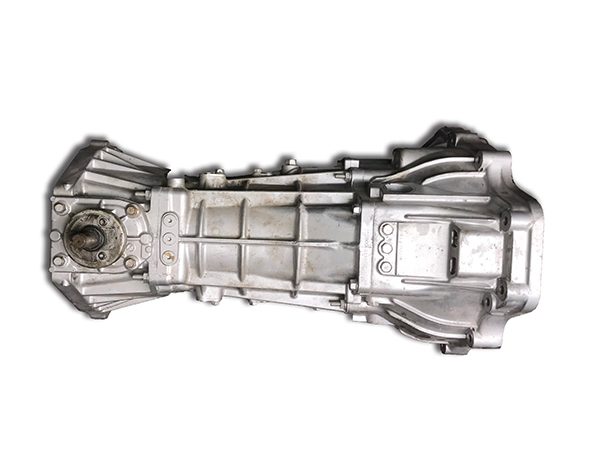
The SOHC 4.0 in the Ford Ranger came with a M5OD-R1-HD manual transmission. It never came with the M5OD-R4 (M5R4). The 2002+ Ford Explorer (not Sport) came with the new M5OD-R4 (M5R4) behind the SOHC 4.0. So it may be that someone will decide to swap one in to a Ford Ranger. Therefore, we present you with this information.
In 2002 Ford introduced a new four-door model of the venerable Explorer and its sister, the Mercury Mountaineer. The manual transmission option for the new four door model is a 5-speed fully synchronized unit designated the M5R4 or M5OD-R4. The M5R1 transmission we all know and love has been replaced by a radical new design built by Mazda. This unit ne resemblance to the M5R1.
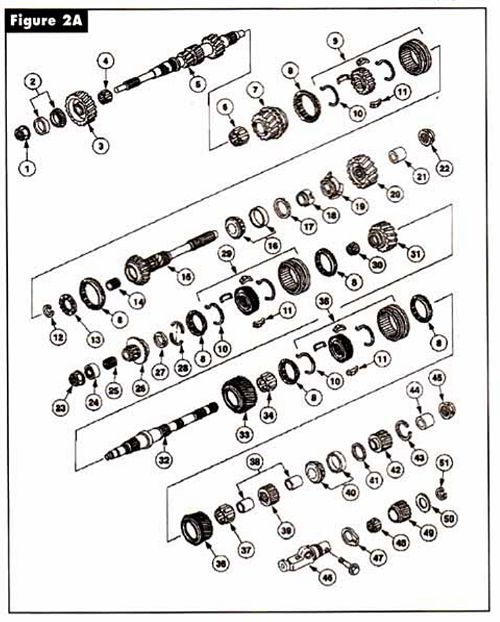
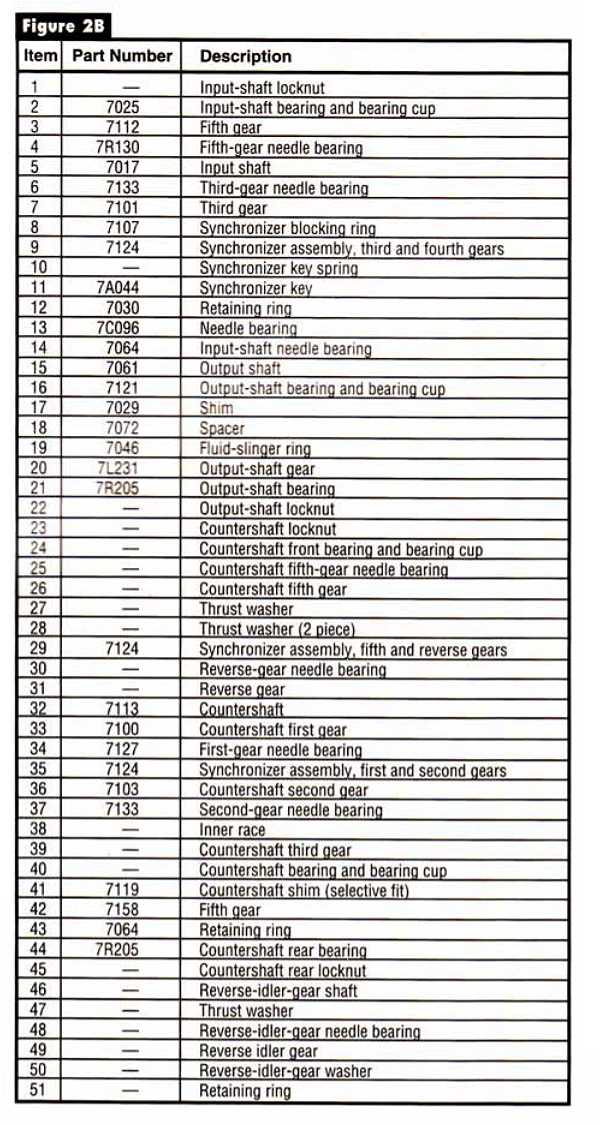
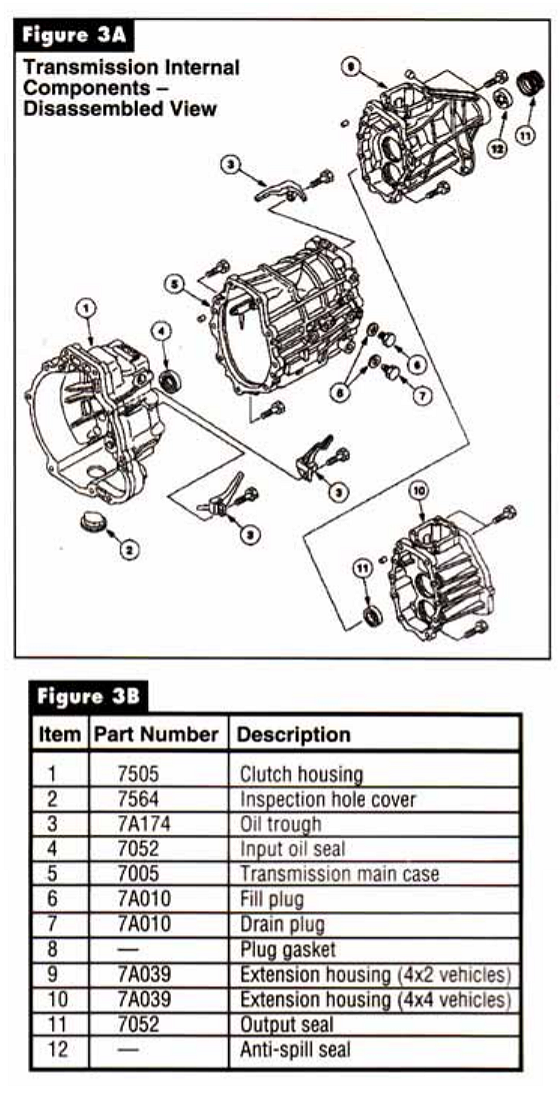
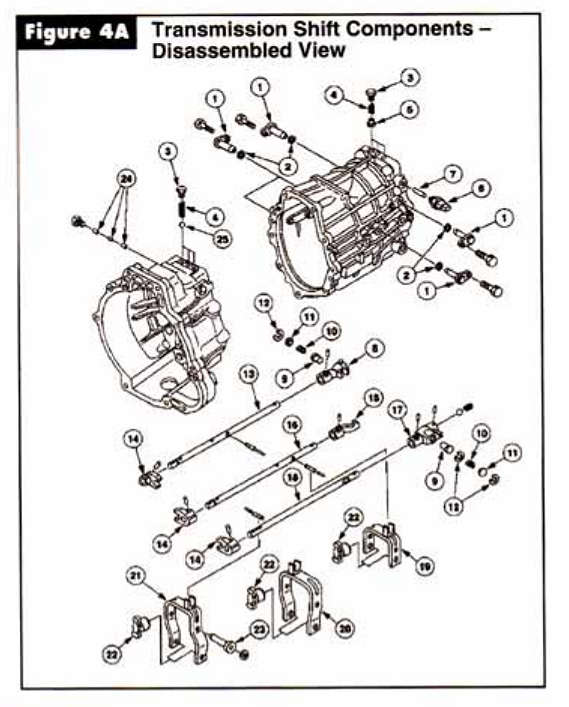
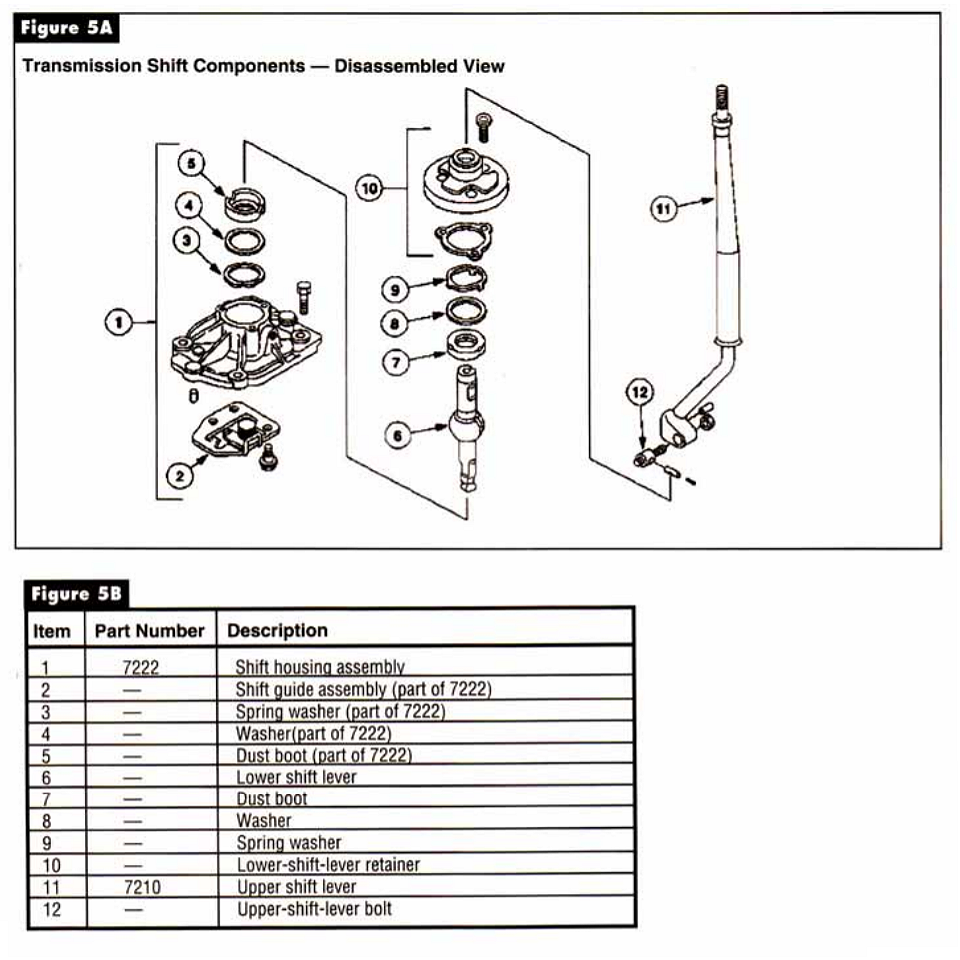
The new model has a detachable bellhousing, a main case and extension housing, all made of aluminum. The mainshaft and countershaft are supported by tapered bearings with shims under the races to set endplay. All speeds are fully synchronized with helical cut gears. The speed gears all run on needle bearings on the shafts. Gone is the removeable shift cover, and all shift components are housed in the main case. Mercon ATF is the lubricant fill specified for the M5R4.
Ratios are:
1st: 3.38
2nd: 2.06
3rd: 1.30
4th: 1.00
5th: 0.79
Reverse = 3.70
The M5R4 represents one of the most radical design changes in rear wheel drive manual transmissions. Traditionally, rear wheel drive manuals have been designed with 4th gear being the input shaft. The input was relatively short, with the drive gear mounted behind the input bearing and a pocket in the input to support the pilot journal of the mainshaft on a needle or tapered bearing. On the M5R1 unit the 3-4 synchronizer assembly is on the mainshaft directly behind the input gear. The 1-2 speed gears and synchronizer assembly and the the 5th and reverse speed gears and synchronizer are mounted on the countershaft.
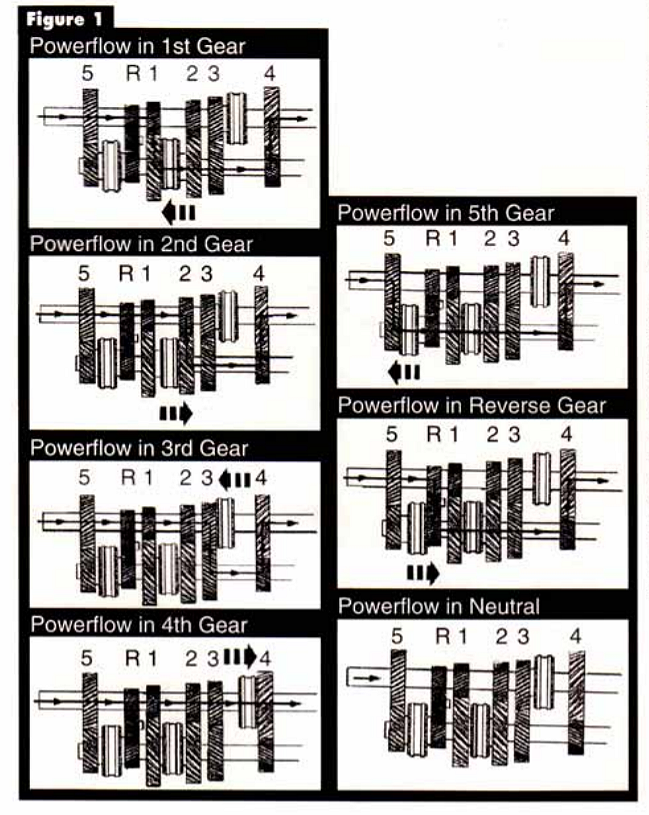
The design of the new M5R4 locates the 5th gear as the the first gear on the input shaft, followed by reverse, 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gears, in that order. At the rear of the input shaft is the 3-4 synchronizer assembly. Fourth gear is part of the shortened output shaft or mainshaft. Mounted on the countershaft are the 5th and reverse synchronizer and speed gears and the 1-2 speed gears and synchronizer assembly. The input gear drives the 5th, 1st, and 2nd gears and the reverse idler gear. We have included a parts illustration and power flow sharts to help you understand how this design works.
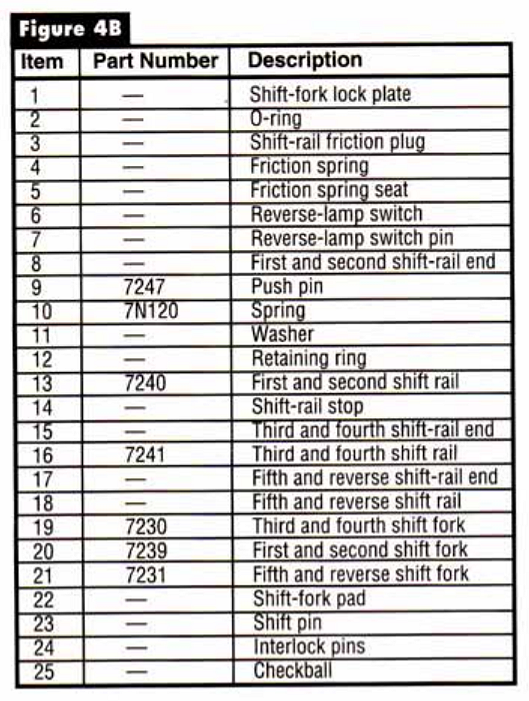
Three stirrup shaped shift forks ride on the shift rails and are positioned by three pairs of shift fork lock plates that are bolted through the sides of the main case. There is a conventional detent and interlock system to give the driver shift feel and to preent engaging two gears at once.
Study the power flow diagrams and parts schematics in Figures 1 through 5, as the diagnostic routines will be very different on the M5R4 because of the unconventional gear placement. We are used to seeing the geartrain mounted from front to back as 4th, 3rd, 2nd, and 1st. Here we have 5th, reverse, 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th. Studying the design we see that the input shaft resembles the design found in a transaxle rather than that in a rear wheel drive truck transmission.
More Photos:
More Diagrams: